
Where there is doubt about a diagnosis of epilepsy, or where the type of seizures someone experiences is unclear, video-telemetry can be helpful. It may help to confirm whether certain symptoms are due to seizures. The patterns on the EEG can be analysed to see if they change when symptoms occur.
You may be asked to keep a diary when you have meals, go to sleep, and have any symptoms which may be a seizure. The wires are connected to a small machine which you wear on a belt (a bit like wearing an mp3 player). The electrodes can usually be hidden under your hair. It uses a portable EEG machine which records the brain's electrical activity when you are going about your normal activities. This may be advised in cases where the diagnosis is not clear. It is done in the same way as the normal test but with you asleep - after the period of 'sleep deprivation'. Therefore, sometimes the EEG test is done after you have stayed awake for all or most of the night. There may be a better chance of detecting abnormal brain activity after a period of time when you are deprived of sleep. You may need to have one of these if your seizures happen when you are asleep or when you are tired. This is usually carried out when you are in hospital. In this test, an EEG is performed while you are sleeping. However, a small number of people have seizures triggered by flickering or strobe lights and so this may help to identify these people.) Sleep EEG This aims to detect if this alters the electrical pattern in the brain. In some cases, a strobe light may be used during an EEG test. Some specialised types of electroencephalograph test Strobe lighting As the EEG pattern in infants and children can vary considerably, careful interpretation of the test is necessary. An adult pattern is usually developed by the age of 15 years. This is because the EEG changes during childhood. The interpretation of a child's EEG recording is more difficult. However, a normal result does not rule out epilepsy, and an abnormal result does not necessarily mean that you have epilepsy. Therefore, if you have symptoms which are thought to be seizures, an abnormal EEG means that the diagnosis is likely to be epilepsy. However, a small number of people who never have seizures and who don't have epilepsy, have some abnormal patterns of electrical activity in the brain.

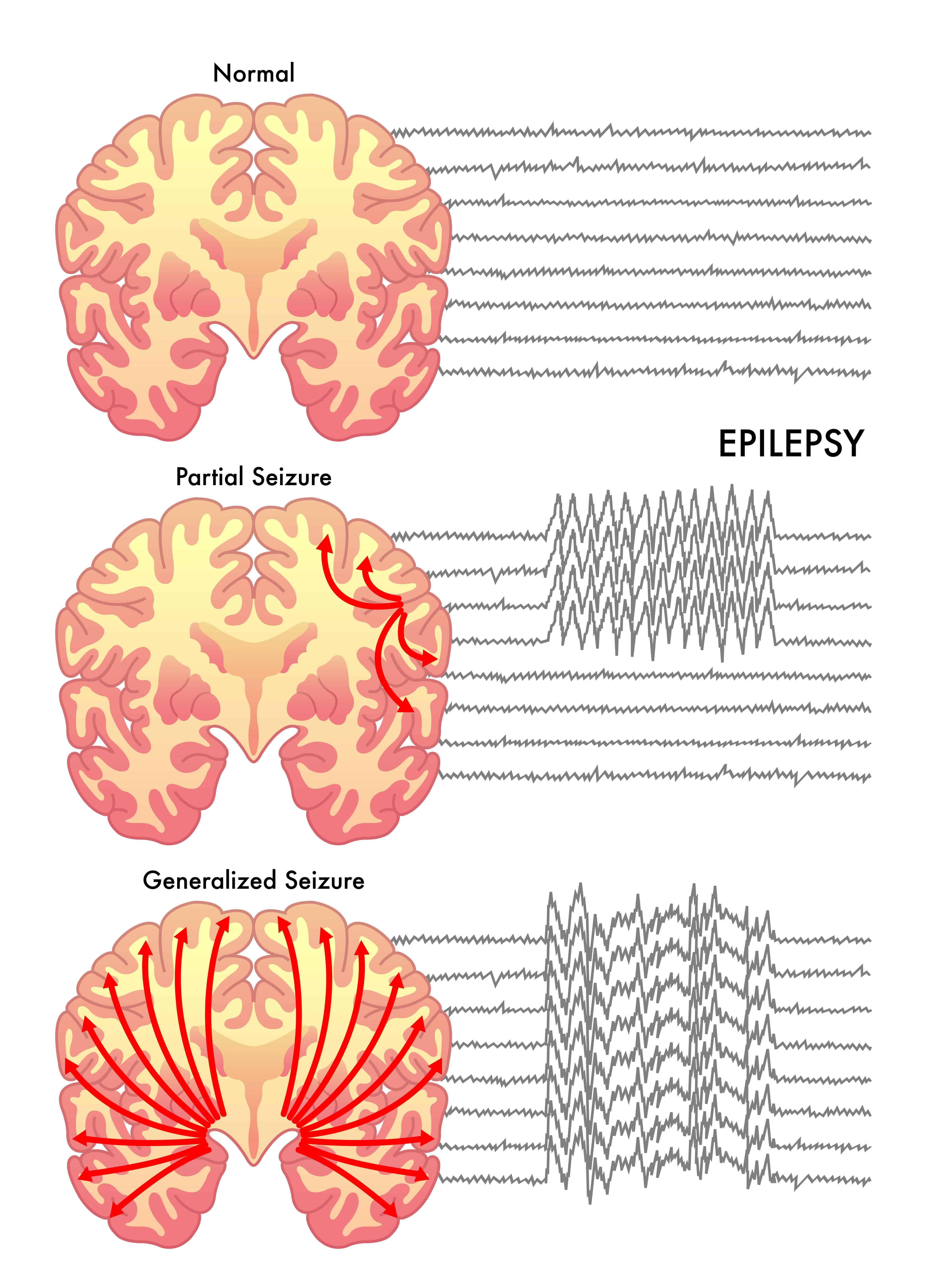
(Although, during a seizure the activity is even more abnormal.) For example, children with typical 'absence seizures' often have a characteristic EEG pattern which helps to confirm this type of epilepsy.

Some people with certain types of epilepsy have abnormal patterns all the time, not just when they have seizures. This shows abnormal patterns of electrical activity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
